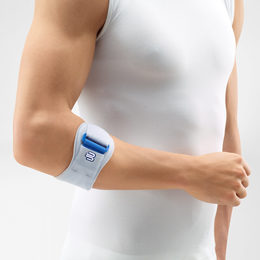
Elbow braces, supports and straps for performance and recovery
Elbow Pain – Causes and treatment options
It’s common for elbow pain to develop if you are building a new garage or spend weeks on end sitting in front of a computer. Muscles become overstrained and tendon attachments get irritated, and rebel. If you listen to your body and protect the painful area, symptoms will quickly subside. But more and more often we are ignoring the signals and carrying on as we were.
Bauerfeind’s medical-grade compression promotes healing blood flow and proprioception to reduce pain, swelling and re-injury. Whether you are recovering from injury or trying to ensure your best performance, Bauerfeind elbow braces stabilize the joints without limiting mobility, so you can rely on your body to get you through the day.
Common Elbow Pain: “Tennis Elbow” and “Golfer’s Elbow”
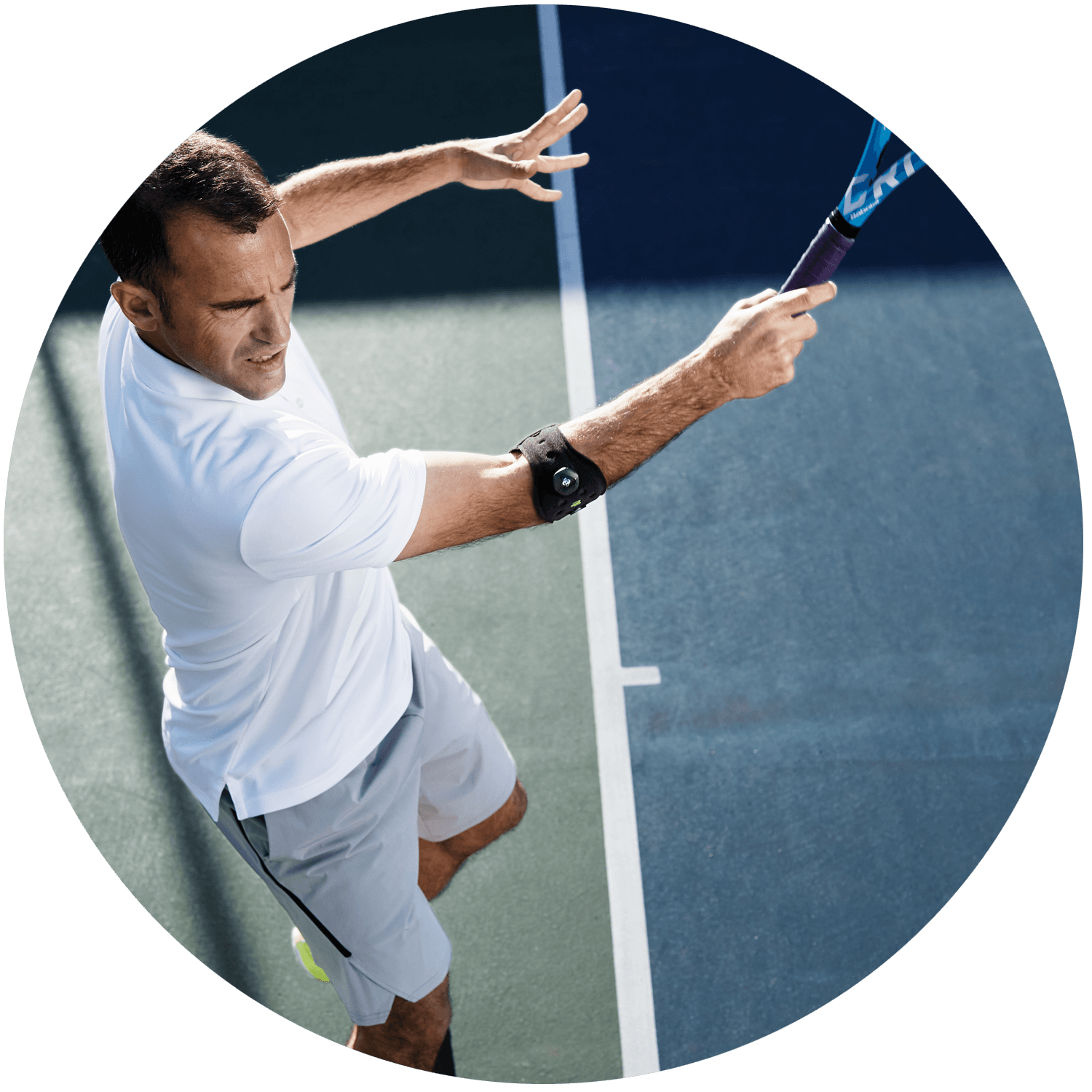
Lateral epicondylitis, commonly known as “Tennis Elbow”, refers to inflammation of the tendons joining the forearm muscles to the outside of the elbow. Symptoms include pain or burning on the outer part of the elbow and weakened grip strength. As the name suggests, Tennis Elbow is common among athletes who play tennis and other racquet sports. However, 90 percent of people affected by tennis arm are craftspeople, musicians or PC users – not tennis players!
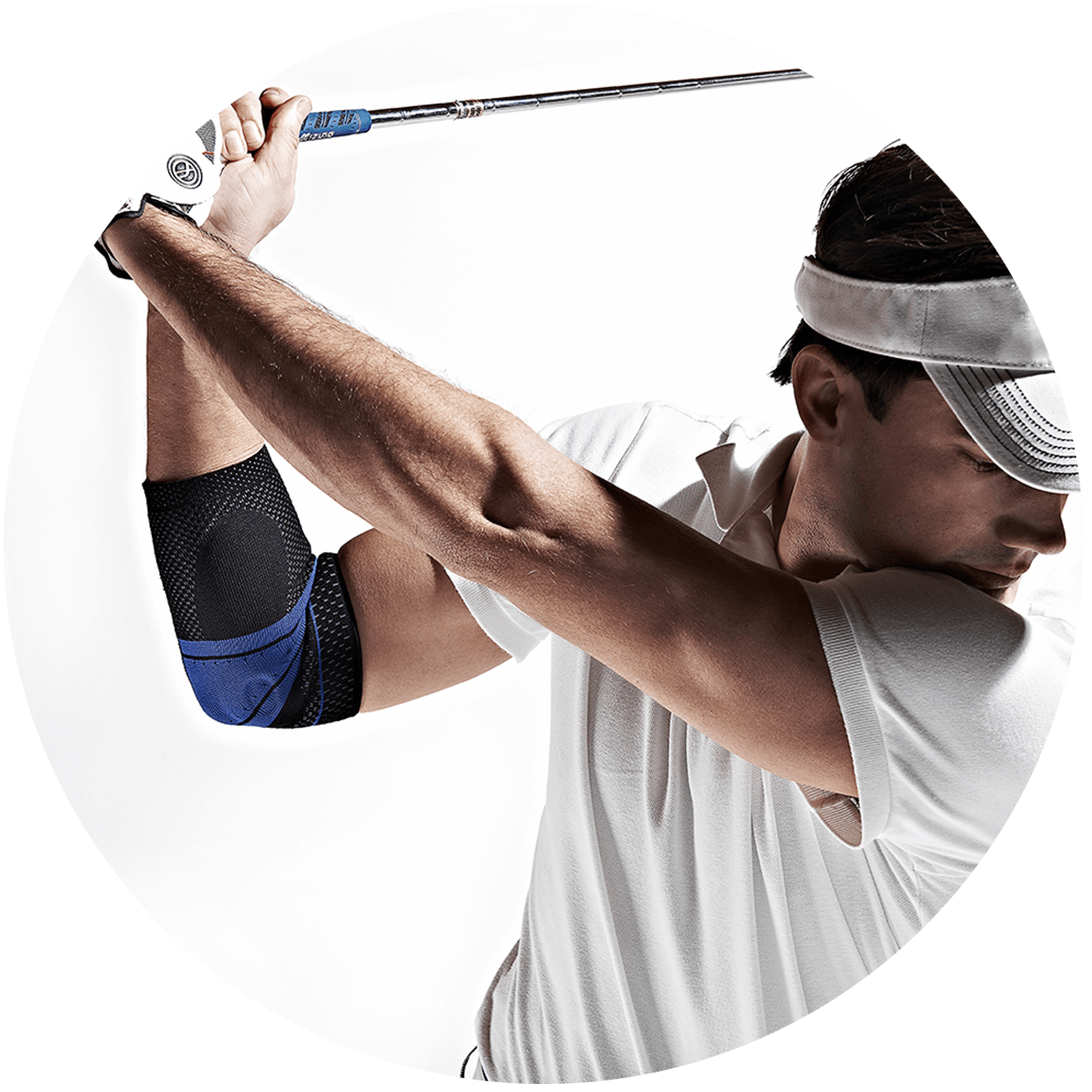


Medial epicondylitis, commonly known as “Golfer’s Elbow”, refers to inflammation of the tendons joining the forearm muscles to the bony bump on the inside of the elbow. Symptoms include pain, stiffness, weakness or in more severe cases numbness and tingling originating at the inner part of the elbow and radiating through the wrist and hand. Golfer’s Elbow is common among athletes who play golf, but it can affect tennis players and others who repeatedly clench their wrists and hands.
Treating Elbow Pain
Wearing a Bauerfeind elbow strap, brace or support with medical-grade compression can help to reduce pain and inflammation associated with tennis or golfer’s elbow. This gives support to the elbow and speeds the recovery and healing process.
Bauerfeind offers 4 products to help prevent or treat this injury: EpiTrain, EpiPoint, Sports Elbow Support and Sports Elbow Strap. For more information, visit the Bauerfeind Elbow Braces page.
Elbow Pain Facts:
- 90 percent of people affected by tennis elbow are craftspeople, musicians or PC users – not tennis players.
- The elbow joint has an unbelievable range of motion: it can extend up to 10 degrees, bend 140 degrees and rotate inwards and outwards by 90 degrees.
- The funny bone is more of a nerve than a bone.
- The development from wooden rackets to graphite tennis rackets took around two decades and, being 30% lighter, the graphite rackets have provided a real relief for the elbow.
- Arm injuries can be primarily caused by damage to the cervical spine in the 5th to 7th cervical vertebra.
Elbow tendonitis, also known as lateral epicondylitis (tennis elbow) or medial epicondylitis (golfer’s elbow), is caused by repetitive stress to the tendons that move and support the elbow and arms. Tennis and golf get a lot of attention for this injury, but anyone doing repetitive tasks with their hands and arms can experience elbow tendonitis.
Most healthcare professionals agree, the first-line treatment for elbow pain is RICE Therapy. RICE stands for Rest, Ice, Compression and Elevation. After an elbow injury it is important to rest the joint by stopping the repetitive movement, put it on ice, apply compression with a medical-grade compression elbow braces or support, and prop it up.
Wearing a medical-grade compression brace from Bauerfeind as part of your treatment of elbow pain can provide the stability and pain relief you need to recover more quickly.
Other treatment options for elbow pain include:
- Over-the-counter drugs like Acetaminophen (name brand Tylenol) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS) like Aspirin, Ibuprofen and Naproxen.
- Arm-strengthening exercises overseen by your doctor or physical therapist
- Elbow injection therapies
- Surgery to remove, repair or replace an injured ligament, tendon or meniscus
As always, it’s best to seek the care of a healthcare professional to determine the best treatment for your elbow pain.