GenuTrain P3 centers and secures the knee cap
Knee sprains are a common injury of one or more ligaments of the knee. It can happen suddenly – you just twisted your knee. In most cases, home remedies can help reduce pain, stabilize the knee and train surrounding muscles for recovery. This article tells you more about treating knee sprains, which knee support is best, and provides tips for injury prevention.
GenuTrain S Knee Brace
Stabilizes the knee, activates the muscles and accelerates the healing process.
With its stabilizing sidebars and adjustable strap system, the GenuTrain S securely supports the knee without limiting mobility. The kneecap is kept centered with a specially shaped round pad, reducing pressure peaks and relieving pain. Together with the medical-grade compression knit, this pad produces pain-relieving massage during movement, reduces swelling and activates the muscles that stabilize the joint.
Treatment options for a knee ligament sprain
The knee joint connects the thigh and calf with a system of muscles, tendons and ligaments. The four ligaments in the knee stabilize the joint with two x-shaped ligaments in the center (ACL) and back of the knee (PCL), and one on each side (MCL, LCL):
Anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) X-shaped ligament located inside the center of the knee
Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) X-shaped ligament located inside the back of the knee
Medial collateral ligament (MCL) Ligament on the inner side of the knee
Lateral collateral ligament (LCL) Ligament on the outer side of the knee
Mild-to-moderate knee sprains usually heal with conservative therapy within 6-8 weeks; However, a complete ligament rupture might require surgery and could take months to recover. After an initial period of RICE Therapy (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), a support such as the Bauerfeind GenuTrain S can help to stabilize the knee, relieve pain, and increase proprioception.
Depending on the severity of your ligament injury, your doctor may also prescribe crutches take your weight off and physical therapy to evenly strengthen your knee muscles. After your knee is completely healed you can keep wearing your GenuTrain S or graduate to the original GenuTrain knee support for extra confidence and injury prevention.
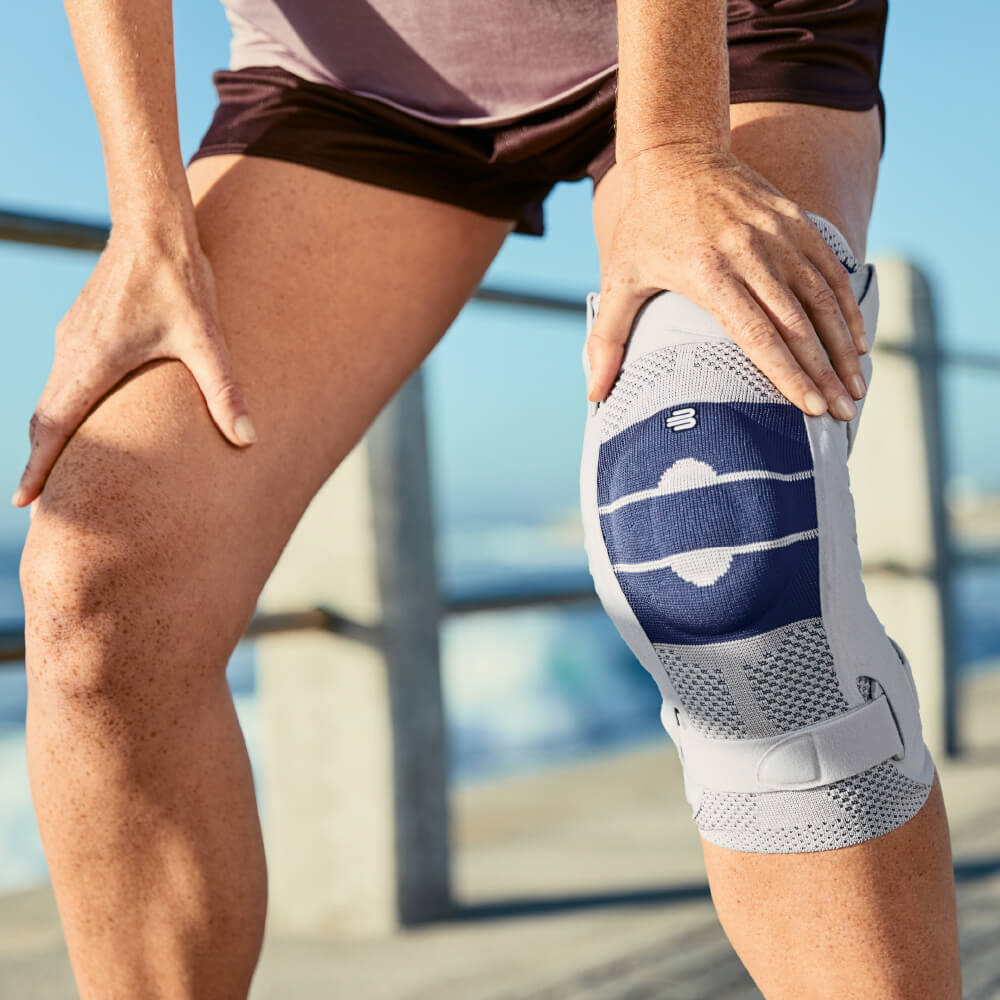

I've used this for some time and also during skiing to support my knees which was damaged some years ago. It gives my knee excellent support. A combination of ordinary training and use of this brace is excelent.
Kim M.

Made for Everyday Use
Extra breathable, moisture-wicking knit material

Improves Confidence
Stabilizes and secures the knee

Low-Profile
Lightweight, low-profile design, can be worn under pants
How to Prevent Knee Sprains
Stretch and strengthen the muscles around your knee to stabilize and keep excessive strain off the joint. All muscles have to work together; inner and outer thighs, as well as quads, need extra attention. Wear the GenuTrain S knee support to help secure and stabilize your knee. Together with your healthcare team you can develop a workout routine that works for you.
- Wear the GenuTrain S knee support – for better proprioception, to stabilize and secure your knee joint while getting back to being active
- Strengthen the muscles around your knee to ease pressure and stabilize the knee joint
- Increase activity gradually
- Warm up before exercising
- Maintain a healthy weight – to keep the stress on your joints low
- Wear appropriate shoes to prevent slips, trips, falls and twists of your knee