Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of hereditary disorders of connective tissue that can influence the body in various ways, as connective tissue provides both strength and elasticity to the underlying structures of your body. Primarily, EDS affects the skin, joints and blood vessel walls of those who have it.
The different forms of EDS can be characterized by:
- Joint hypermobility (which is most common)
- Joint instability, dislocations, scoliosis
- Skin hyperextensibility
- Abnormal scarring and other structural weaknesses
In rarer cases of EDS, people also experience a weakness of specific tissues that can lead to gum, dental or eye diseases, as well as cardiac valve and aortic root disorders.
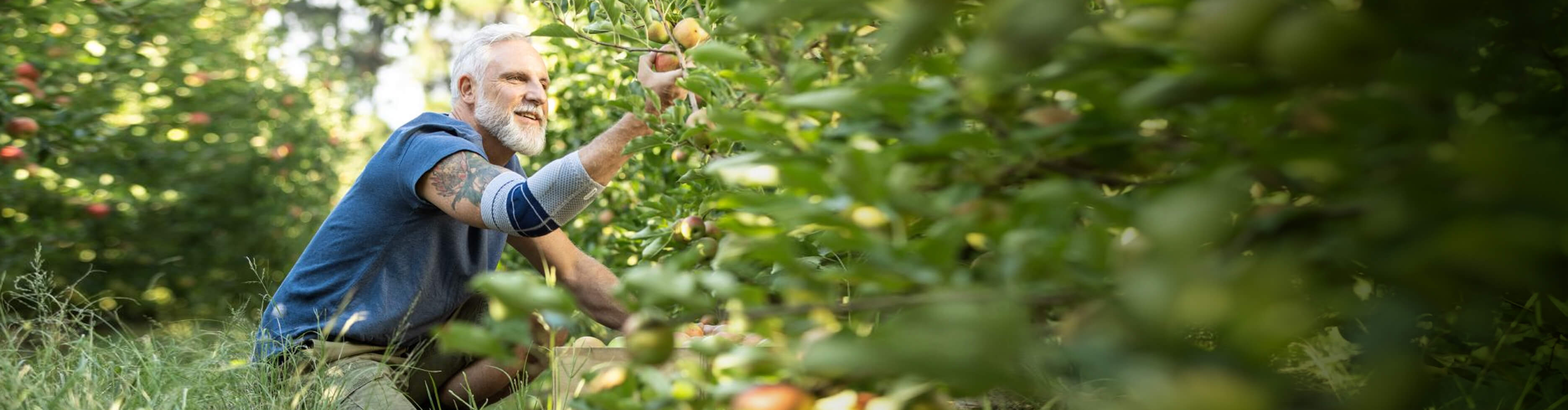

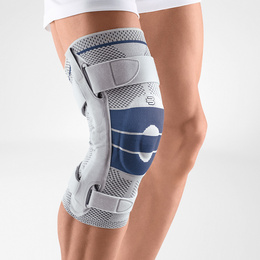
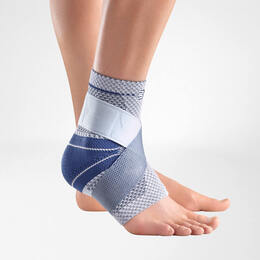
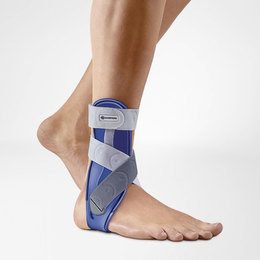
How Bauerfeind can help with EDS joint pain and instability
Joint pain, fatigue and instability are common in people living with EDS, so braces and supports are used as a way to help improve treatment and the everyday quality of life. Many people with EDS own braces for nearly all areas of their body and even use them while active or inactive.
Bauerfeind’s line of premium EDS braces and supports are recommended to patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome because of their stability, comfort and lightweight design. Our braces are anatomically contoured with a special knit fabric that provides medical-grade compression and more breathability for all-day wearing comfort.

Comfortable To Wear
Made of breathable and skin-friendly materials

Stabilization & Support
For joints and muscles without limiting mobility

Low-profile
Lightweight, low profile design, can be worn under clothing